I have recently tested some remote administration tools for Ubuntu server (or any other Linux-based server). I have recorded here my findings and installation steps.
I have recently tested some remote administration tools for Ubuntu server (or any other Linux-based server). I have recorded here my findings and installation steps.
Today I present Monit, a monitoring and control tool for Unix and Unix-like systems.
This article will be followed by others with different tools. Stay tune, and you can find them all using the following tag remote-server-admin.
Monit – Server monitoring
Monit offers basic system monitoring and can act on predefined alerts.
Installation
As simple as
$ sudo apt-get install monit
Configuration
You need to edit the file /etc/monit/monitrc I modified the following lines:
set httpd port 2812 and # use address localhost # only accept connection from localhost # allow localhost # allow localhost to connect to the server and allow admin:monit # require user 'admin' with password 'monit' # allow @monit # allow users of group 'monit' to connect (rw) # allow @users readonly # allow users of group 'users' to connect readonly
This allows Monit to be monitored via a web browser from a remote machine using the credentials admin/monit.
Activate monitoring
In the same configuration file (/etc/monit/monitrc) there is a section called Services where some template monitoring services are defined. Simply uncomment those that interest you. I uncommented those two:
Monitoring the CPU resources
check system ubuntu-storage if loadavg (1min) > 4 then alert if loadavg (5min) > 2 then alert if memory usage > 75% then alert if swap usage > 25% then alert if cpu usage (user) > 70% then alert if cpu usage (system) > 30% then alert if cpu usage (wait) > 20% then alert
Monitoring my NAS server
check host sogur with address 192.168.1.2 if failed icmp type echo count 3 with timeout 3 seconds then alert
Monitoring specific services and controlling them
Reading this resource at How to Forge regarding Munin and Monit installation, I did the following configuration. I created a new file
$ sudo vi /etc/monit/conf.d/sshd
And added the following configuration in it:
check process sshd with pidfile /var/run/sshd.pid start program "/usr/sbin/service sshd start" stop program "/usr/sbin/service sshd stop" if failed port 22 protocol ssh then restart if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
Activating the new configuration
We need to restart the monit service:
$ sudo service monit restart
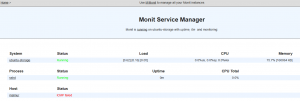
Visualising Monit
Open your favorite web browser and go to the page http://IP:2812 Example: http://192.168.1.2:2812